Best Practice for Gaming Gateway of Higress × OpenKruiseGame
Author: Weiji Zhao/ChrisLiu/Tianyi Zhang
Time: 2024-01-24
OpenKruiseGame (OKG) is an open source game service Kubernetes workload for multi-cloud, which is a sub-project of CNCF's workload open source project OpenKruise in the gaming domain, and it provides common game service management functions such as hot update, in-situ upgrade, and targeted management. As a typical traffic-intensive scenario, gaming puts high demands on the ingress gateway in terms of throughput, latency performance, elasticity and security.
Higress is a next-generation cloud-native gateway built on the open source Istio and Envoy, based on more than two years of Envoy gateway practice within Ali, Higress realises a three-layer gateway, namely, security gateway, traffic gateway, and microservices gateway, which significantly reduces gateway deployment and operation and maintenance costs. Higress can be used as an Ingress entry gateway for K8s clusters, and is compatible with a large number of K8s Nginx Ingress annotations, allowing for a smooth migration from K8s Nginx Ingress to Higress, and also supports the K8s Gateway API standard, which allows for a smooth migration from the Ingress API to the Gateway API.
In this article, we will demonstrate how Higress seamlessly interfaces with OKG Gaming Services, and the outstanding features it brings to the table.
Higress Seamless Access OKG
Preceding Steps:
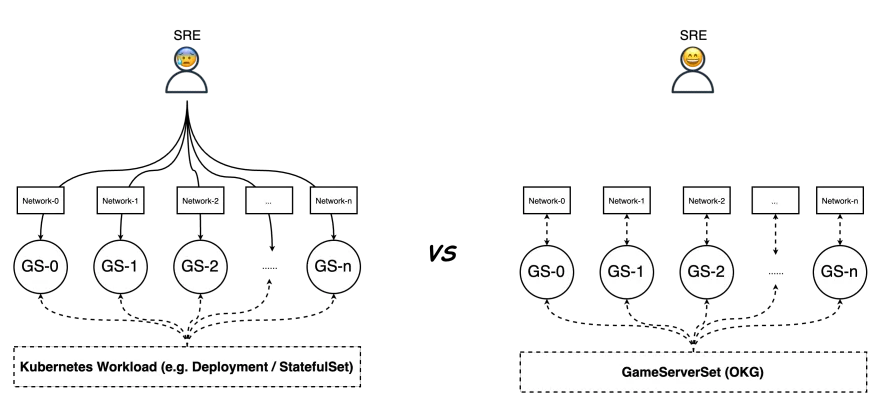
OKG provides a number of excellent features for hot updating and scaling game services, which makes it easy for game operators to manage the full life cycle of game services. Gaming is different from stateless services in that the network traffic of player battles is not allowed to be load balanced, so each game service needs a separate access address.
When using native workloads (such as Deployment or StatefulSet), Ops engineers need to configure the access layer network for each of the many game suits, which undoubtedly hampers the efficiency of the service launch, and manual configuration invariably increases the probability of failures. gameServerSet workloads provided by OKG automate the management of the access network of game suits, greatly reducing the burden on Ops engineers. This greatly reduces the burden on operation and maintenance engineers.
For TCP/UDP network games, OKG provides network models such as HostPort, SLB, NATGW, etc. For H5/WebSocket type network games, OKG also provides Ingress network models accordingly, such as Higress, Nginx, ALB, etc.
This article uses an open source game Posio to build a demo game suit. In the following configuration, IngressClassName="higress" specifies Higress as the network layer of the game service. Higress can seamlessly access the Posio game service through the following configuration, and can implement the higher-order traffic management defined by Higress based on the Annotation. Example Yaml As shown below, the GameServerSet generates the access domain name for the game service associated with the game service ID.
In this example, game 0 is accessed from the domain name game0.postio.example.com, and game 1 is accessed from the domain name game1.postio.example.com. This is how the client accesses the different games.
piVersion: game.kruise.io/v1alpha1
kind: GameServerSet
metadata:
name: postio
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1
updateStrategy:
rollingUpdate:
podUpdatePolicy: InPlaceIfPossible
network:
networkType: Kubernetes-Ingress
networkConf:
- name: IngressClassName
value: "higress"
- name: Port
value: "5000"
- name: Path
value: /
- name: PathType
value: Prefix
- name: Host
value: game<id>.postio.example.com
gameServerTemplate:
spec:
containers:
- image: registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/chrisliu95/posio:8-24
name: postio
OKG horizontal scaling provides automatic scaling, scaling according to the OpsState of the game service, scaling according to the DeletionPriority, scaling according to the serial number of the game service, and so on, in order to support the business requirements of the game operation and maintenance. While the horizontal scaling feature brings convenience to game developers, it also puts forward higher requirements for the entry gateway: the entry gateway must have the ability to hot update the configuration and complete the smooth distribution of routing configuration. The reason is that when expanding the game service, OKG will create Ingress and other related network resources synchronously to ensure the automatic launch of the game service. If the ingress gateway does not have the ability to configure hot updates, online players will experience disconnections during expansion, which will affect their playing experience.
Nginx Reload Does Not Grace Hot Updates
In the event of expansion of the game service or a change in the defined routing policy, a configuration change in Nginx triggers a reload, which results in both upstream and downstream connections being disconnected and triggering a reconnect.
Let's take the Posio game service as an example to simulate the problem that occurs when Nginx+OKG expands the game service.The Posio server relies on socket connections to communicate with clients. When the game service expands, it triggers the creation of the corresponding Ingress resource, at which time Nginx-ingress-controller listens to the Ingress resource change and triggers its own reload mechanism, at which time the original connection with the game service (such as the Socket connection in this example) will be disconnected. The physical sensation on the player's side of the game is that there is abnormal lag.
To visualise the impact of the Nginx Ingress reload, we made some changes to the Nginx default configuration parameters:
kubectl edit configmap nginx-configuration -n kube-system
data:
...
worker-shutdown-timeout: 30s # A difficult configuration to weigh.
The Nginx configuration parameter worker-shutdown-timeout is a timeout for the Nginx worker process to gracefully go offline. The worker process will first stop receiving new connections and wait for the old connections to be gradually closed, and only after the timeout has been reached will the worker process forcefully shut down all the current connections, completing the exit of the process.
If this parameter is configured too small, it will cause a lot of active connections to be disconnected instantly; if this parameter is configured too large, it will cause long websocket connections to always maintain the Nginx process, and when frequent reloads occur, it will generate a large number of shutting down worker processes, and the memory occupied by the old workers will not be freed up, which may lead to OOM. This can lead to online failures:
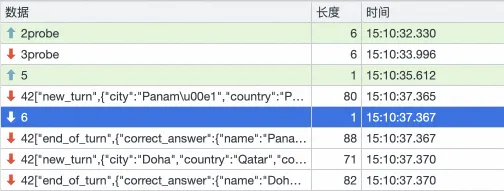
The actual playing process is as follows: the client accesses the game service and plays normally. During this process, we triggered the expansion of the game service through OKG capability, and checked the response of the client at this time. Through the web developer tool, we can see that there are two socket connections, one is established by the original browser accessing the game service, and the other is a socket connection generated by Nginx disconnecting and then reconnecting.
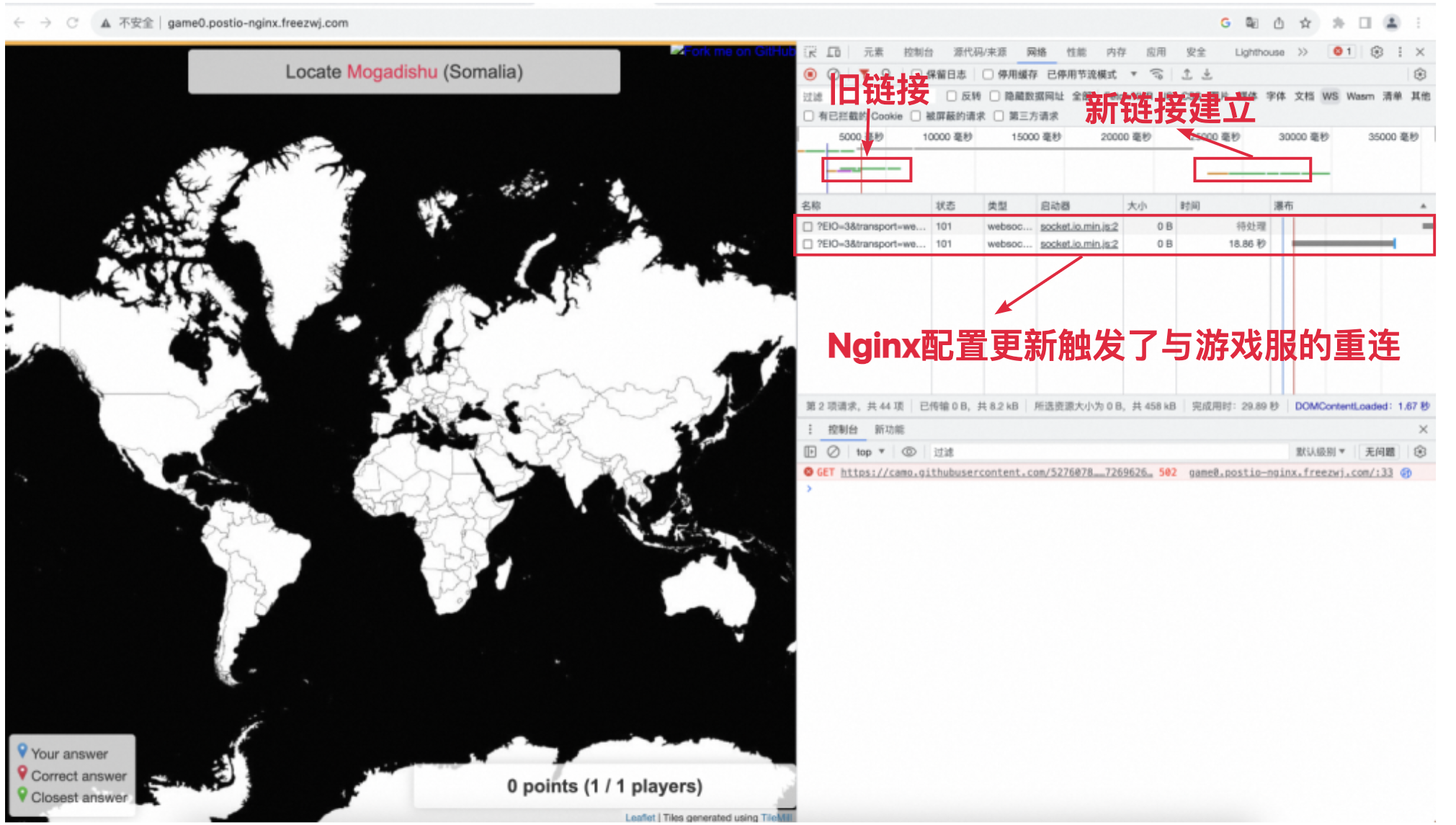
The timestamp of the last packet received by the original connection is 15:10:26.
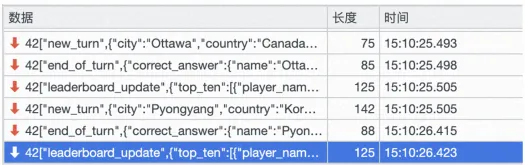
The time between the creation of the new connection and the acquisition of the first normal game package was 15:10:37, and the disconnection between the web page and the game service lasted about 5s.
In addition to the player's playing experience is affected, this mechanism will also give the overall stability of the business mine. In high concurrency scenarios, because the connection is instantly broken, resulting in a large number of concurrent client reconnections, will lead to an instantaneous spike in the CPU of Nginx; and the back-end game servers need to deal with more business logic, the general demand for resources than the gateway is higher, so a large number of concurrent reconnections transmitted by Nginx is more likely to defeat the back-end, resulting in an avalanche of business.
How Higress Achieves Elegant Hot Updates
Higress supports the use of K8s Ingress to expose the external IP ports of the game server for players to connect to. Higress supports hot updating of routing configurations when the gaming service scales or defined routing configurations change to ensure stability of player connectivity.
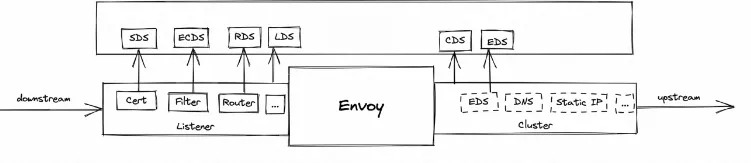
Higress' precise configuration change management based on Envoy enables real dynamic hot update of configuration. downstream corresponds to listener configuration in Envoy and upstream corresponds to cluster configuration in LDS. In Envoy, downstream corresponds to the listener configuration, which is handed over to LDS for configuration discovery, while upstream corresponds to the cluster configuration, which is handed over to CDS for configuration discovery. downstream connection will only be disconnected when the listener configuration is updated and rebuilt, and will not affect the upstream connection; The downstream and upstream configurations can be changed independently without affecting each other. Further, the certificate, filter plugin and router under listener can be changed independently, so that no matter the certificate/plugin/route configuration is changed, it will no longer cause the downstream connection to be disconnected.
Precise configuration change mechanism, in addition to Envoy can achieve real hot update, also makes the Envoy architecture more reliable, Envoy configuration management from the beginning of the design for the separation of the data plane (DP) and the control plane (CP) designed for, so the use of gRPC to achieve the remote configuration of the dynamic pull, and with the help of the proto to standardise the configuration fields, and to maintain the version of the compatibility. This design enhances the security of the architecture by separating the security domains of the data plane and the control plane.
After using OKG to access Higress, the following simulation still simulates the client accessing the game service and playing normally. During this process, the OKG capability triggers the expansion of the game service, and we can see the response of the client at this time. As you can see from the web developer tool, the connection between the client and the game service is stable and unaffected during this process.
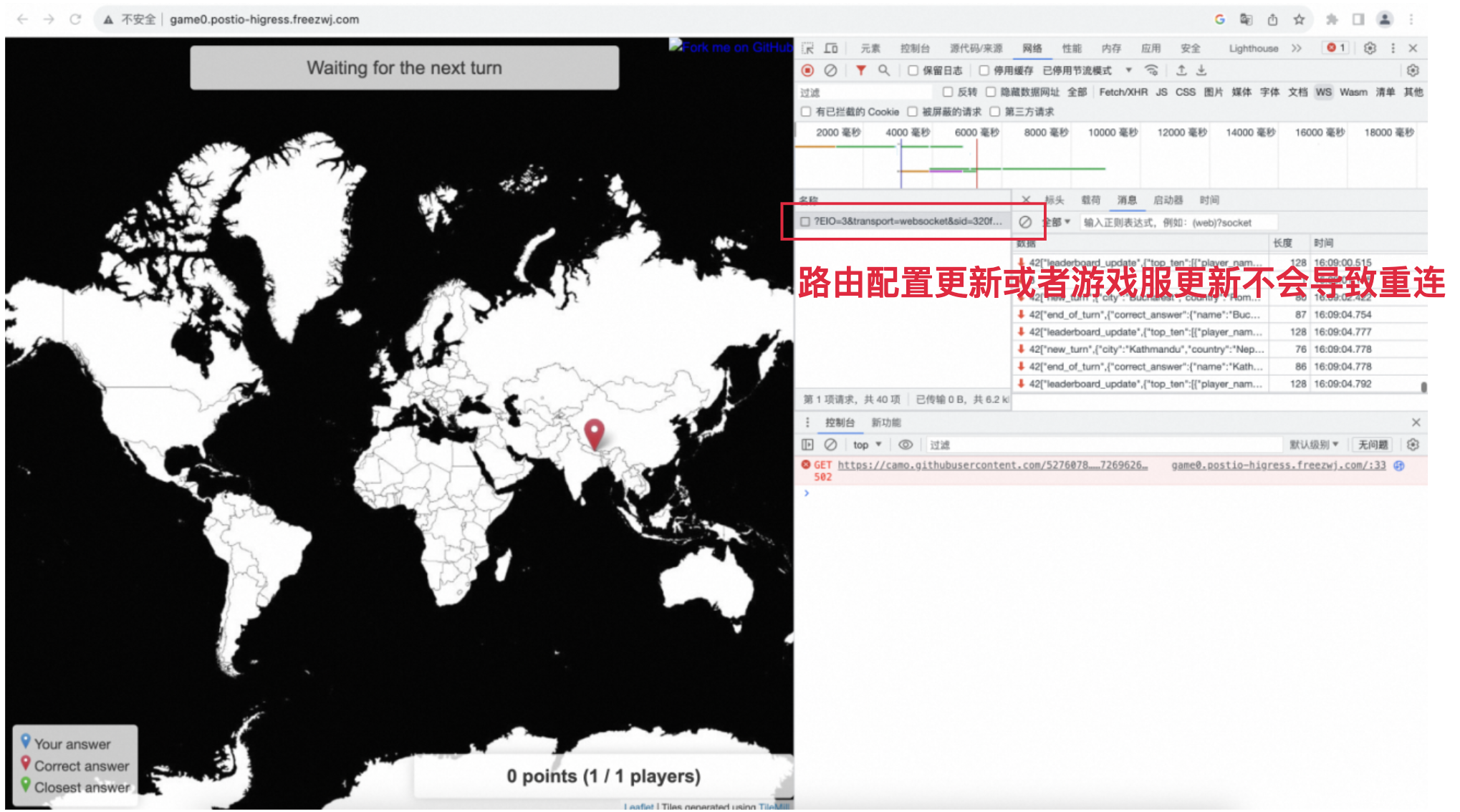
In addition, in a large-scale game server scenario, each game server corresponds to a separate Ingress, which generates a large amount of Ingress resources, and we tested that at a scale of 1k, it takes minutes for Nginx Ingress to take effect in order to expand a game server, whereas Higress can take effect in seconds.This problem with Nginx Ingress was also addressed by This issue with Nginx Ingress was also addressed by Sealos, and was eventually resolved by switching to Higress, which you can read about in this article:《云原生网关哪家强:Sealos 网关血泪史》